A Fine Wee Broxburn Pug
Boxburn, Powflats, Roman Camps
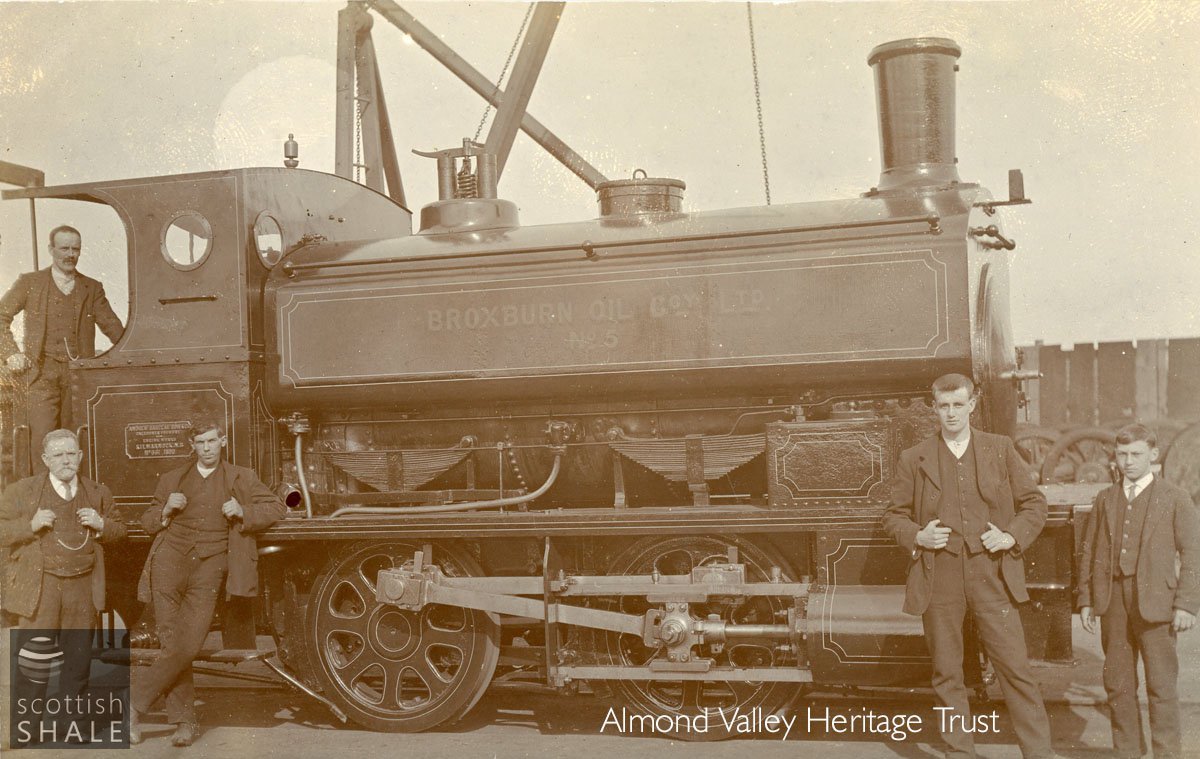

Broxburn Oil Company No.5, seemingly with proud crew and gaffer. The spotless condition suggests the photograph was taken not too long after the pug was built in 1890.
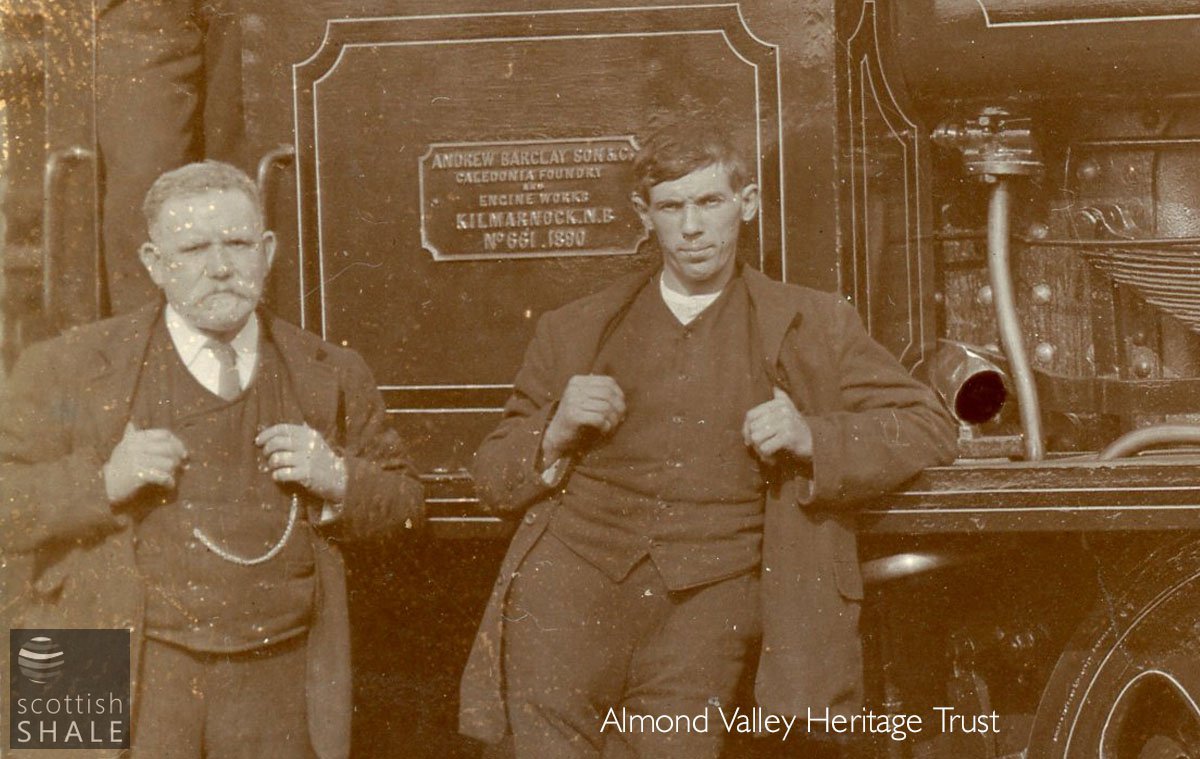

Fierce pride.
F19016, first published 11th January 2020
Busy little shunting locomotives, and their trains of wooden wagons, were once a familiar part of industrial landscapes. Whistles and shrieks, the thud of buffers and the clang of couplings contributed to the soundtrack of everyday life in many mining districts. While many of these industrial “pugs” spent an unadventurous life confined to a works yard, the pug engines of the Broxburn Oil Company had free reign over a network of mineral railways criss-crossing the West Lothian countryside, linking shale mines to the company’s oil works and refinery.

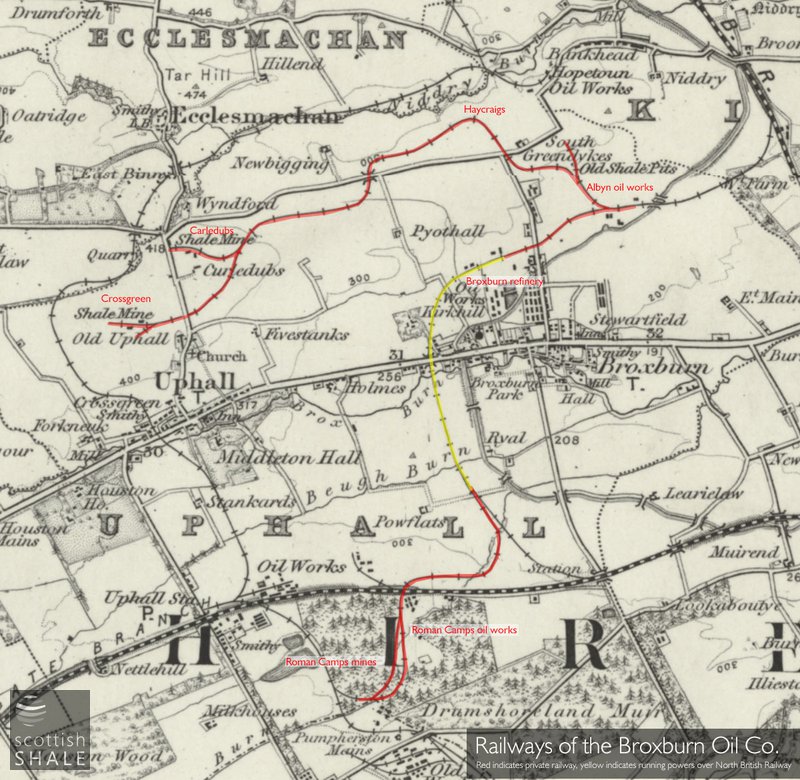
In 1877, when the Broxburn Oil Company began construction of their new Albyn oil works, a branch railway from the main line near Ratho was already in place; installed earlier to serve various defunct oil works. The Broxburn company bought their first two locomotives at that time, presumably using these to draw trains of shale from local pits to the oil works, and to convey tanks of crude oil from these works to their refinery. The Albyn oil works and the Broxburn refinery were rather inconveniently constructed either side of the Greendykes Road, and frequent shunting of trains over the level crossing caused annoyance to road users for many years.
As the company grew, it looked further afield for supplies of shale. In 1888, new mines were opened at Carledubs, close to the road from Uphall to Ecclesmachan. The company built a mile and a half of railway line to link the mines to their works, following a delightfully circuitous route through picturesque countryside by way of Haycraigs and Greendykes. Within a few years the line was extended further westward to new shale mines at Crossgreen; requiring a further level crossing.

The company also secured shale reserves to the south, beneath Drumshoreland moor. It came to agreement with the North British Railway to construct a branch from Drumshoreland station to Holygate and the Broxburn refinery. This was then used for dispatch oil products to the west of Scotland. As part of this deal, the oil company was allowed to run their pug engines along part of this line to serve shale pits in the Roman Camps area and, from 1894, to the Broxburn company’s new Roman Camps oil works.
To handle this growing traffic, the company bought further pugs; a total of eight being acquired by the outbreak of WW1. These were all little four-wheeled saddle tanks of the usual Scottish design; all except one built by the Kilmarnock firm of Andrew Barclay & Sons.
Most of what we know about the operation of these railways come from accounts of accidents and mishaps. It seems that miners were often transported to work in some form of railway carriage. In 1893 Henry Farrow, a resident of Old Holygate, was waiting to board a carriage conveying workmen to the Roman Camps pits. He seems to have been standing nonchalantly with one foot on the rails when one of the Broxburn Oil Company pugs emerged out of the darkness, knocking him over and fatally fracturing his spine.
The gradient from Holygate down to the Beugh Burn near Powflats Farm, and steep climb upwards towards Roman Camps, caused many operational problems. In 1904, seven large wagons that had been left standing at Roman Camps mysteriously started to run away down the steep gradient towards Broxburn. Newspaper accounts suggested that they achieved a speed of 75 or 80 mph (!), before being diverted by catch points protecting access to the Holygate branch. The wagons ploughed on across fields for a further 60 yards before coming to a halt undamaged. Later that day, three of the Broxburn Oil Company’s locomotive arrived on the scene and pulled the wagons back onto the track.
A much less happy incident occurred in June 1923. One of the Broxburn Oil Company pugs, hauling nine wagons of shale from Roman Camps No.3 pit, was heading down the gradient towards Powflats farm when it began to slip on the greasy rails. Despite pinning down many of the wagon brakes, the driver had to resort to putting his engine in reverse in an effort to slow the train. As he struggled to bring his train under control, he saw another of the Broxburn company’s pugs slowly approaching on the same line. Whistles were blown, arms waved furiously, and the approaching engine was placed in reverse. This however failed to prevent a collision between the two pugs and the derailment of most of the wagons. Most jumped from the footplate immediately prior to impact, but Robert Davie, driver of the approaching engine, seems to have stayed at his post. His lifeless body was later found at the track side.